Introduction
The effects of an enlarged prostate can significantly impact a man’s life as he ages. An enlarged prostate, medically known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition among aging men. This occurrence, although not linked to cancer, can lead to various symptoms and challenges that affect both the individual and those around him.
Understanding the Enlarged Prostate
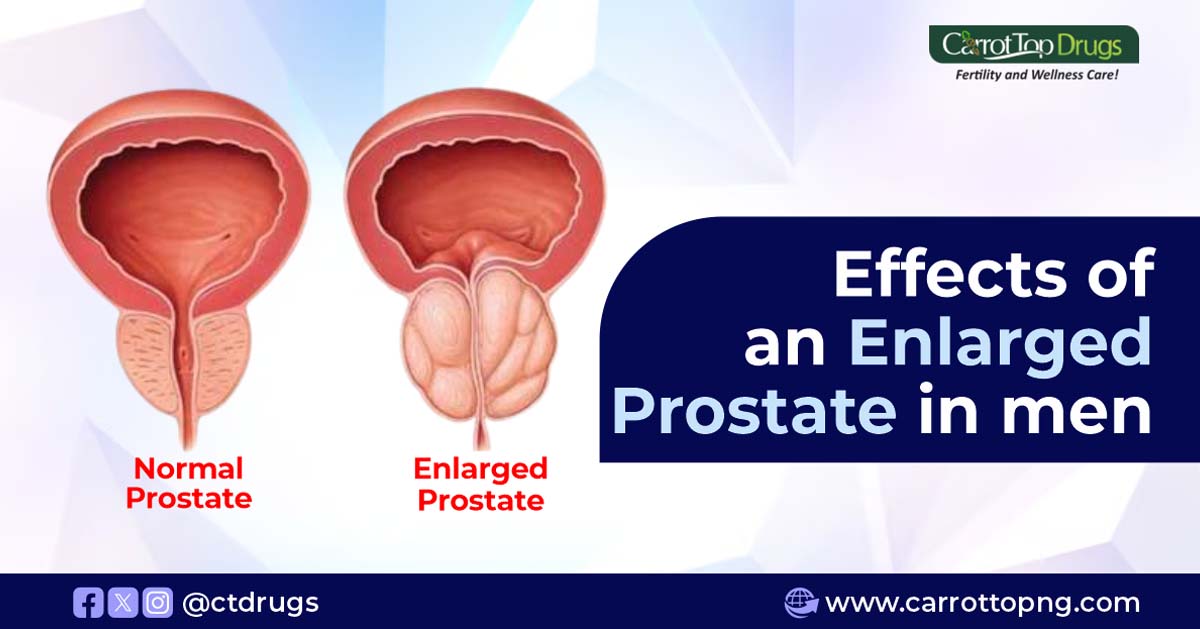
An enlarged prostate is a prevalent condition among aging men, officially known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Typically, the effects of an enlarged prostate start to manifest when the prostate gland undergoes abnormal growth, surpassing its usual size. It’s crucial to emphasize that this growth is distinct from cancer, yet it can result in a range of bothersome symptoms.
These effects of an enlarged prostate stem from the gland pressing against the urethra, disrupting normal urinary flow and function. While non-cancerous, the effects of an enlarged prostate shouldn’t be underestimated, and understanding this condition is the first step towards effective management.
The Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
Increased Frequency of Urination:
As the prostate gland enlarges, it exerts pressure on the urethra, causing irritation and making it difficult for a man to empty his bladder fully. Consequently, this triggers a heightened need to urinate more frequently, particularly during the night. This unsettling effect of an enlarged prostate can disrupt normal sleep patterns and impact daily activities.
Urgency to Urinate:
The effects of an enlarged prostate often manifest as a sudden and compelling urge to urinate. This symptom, known as urgency, is a result of the prostate squeezing the urethra, creating an uncomfortable sensation of needing to empty the bladder immediately. The urgency to urinate can lead to hurried trips to the restroom, affecting work productivity and causing anxiety.
Other symptoms are:
- Weak Urine Stream
- Difficulty Initiating Urination
- Feeling of Incomplete Emptying
- Urinary Retention
- Hematuria
How to Detect an Enlarged Prostate Early
1. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE):
One of the primary methods to detect the effects of an enlarged prostate early is through a digital rectal exam (DRE). During this examination, a healthcare professional inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland. By evaluating the size, shape, and texture of the prostate, the doctor can identify signs of enlargement or abnormalities. A DRE is a valuable tool in early detection, allowing for a physical assessment of the prostate’s condition.
2. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test:
Another essential aspect of early detection is the PSA blood test. The PSA test measures the amount of this protein in the blood, helping healthcare professionals monitor any changes over time. Elevated PSA levels can prompt further investigations, aiding in the early detection and proactive management of an enlarged prostate.
3. Imaging Studies (Ultrasounds and MRI):
Utilizing imaging studies like ultrasounds and MRI scans is crucial for early detection of the effects of an enlarged prostate. Ultrasounds use sound waves to create an image of the prostate, providing valuable insights into its size and condition. MRI scans offer a more detailed view, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the prostate’s structure and detect any abnormalities.
Importance of Early Detection
1. Timely Treatment and Management:
Detecting the effects of an enlarged prostate early holds paramount importance as it facilitates timely treatment and management strategies. Proactivity in identifying an enlarged prostate allows healthcare professionals to design a targeted treatment plan based on the individual’s specific condition. This early intervention can effectively alleviate symptoms and impede the progression of the condition, potentially averting further complications.
2. Enhanced Quality of Life:
Early detection significantly enhances the overall quality of life for those grappling with the effects of an enlarged prostate. Managing the condition in its early stages alleviates discomfort and inconvenience associated with symptoms like frequent urination, weak urine stream, or the persistent feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
3. Prevention of Complications:
Early detection plays a crucial role in preventing potential complications arising from the effects of an enlarged prostate. As the condition progresses, complications can escalate in severity and become increasingly challenging to manage. Late-stage complications may include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, or even kidney damage.
4. Cost-Efficiency in Treatment:
Early detection proves to be more cost-effective in the long run. Detecting the effects of an enlarged prostate at an early stage allows for less invasive treatment options, reducing the financial burden on both individuals and the healthcare system.
Implications of Late Detection
1. Advanced Stage Challenges:
Late detection of the effects of an enlarged prostate presents challenges directly related to the advanced stage of the condition. At this point, the prostate gland is significantly enlarged, often leading to more pronounced and distressing symptoms. Advanced enlargement may result in complications such as acute urinary retention, a condition where one is unable to urinate, necessitating urgent medical attention.
Other complications of late detection are:
- Increased health risks
- Limitations of the treatment options
- It negatively affects emotional health
Impacts of Enlarged Prostate
Some of the common impacts of an enlarged prostate on men are:
1. Urinary Retention and Incontinence
2. Kidney Damage
3. Sleep Disturbances
4. Decreased Physical Activity
5. Impact on Intimate Relationships
6. Reduced Work and Productivity
7. Negatively Affects Emotional Well-being
8. Social Limitations
9. Dietary Adjustments
10. Travel Challenges
11. Financial Costs
12. Routine Disruption
Treatments
1. Medications
Medications are a common first-line approach to managing the effects of an enlarged prostate. Alpha-blockers relax the muscles around the prostate and bladder neck, relieving symptoms like weak urine stream and frequent urination. Another group of drugs, 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, help shrink the prostate over time by reducing the levels of hormones that contribute to its growth. These medications can effectively alleviate the effects of an enlarged prostate by improving urinary flow and reducing bothersome symptoms.
2. Open Prostatectomy
Open prostatectomy is a traditional surgical procedure used for managing severe effects of an enlarged prostate. It involves removing the obstructing prostate tissue through a lower abdominal incision. While it’s more invasive than other options, open prostatectomy is highly effective, especially for individuals with very large prostates.
2. Minimally Invasive Procedures
Several minimally invasive procedures can effectively manage the effects of an enlarged prostate. Some of them are:
Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT) involves delivering microwave energy to the prostate, heating and destroying excess tissue.
Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA), where radiofrequency energy is used to ablate prostate tissue.
3. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is an increasingly popular and effective option for managing the effects of an enlarged prostate. Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) and Photoselective Vaporization of the Prostate (PVP) are common procedures.
Other procedures are:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP)
- UroLift
- Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)
- Water Vapor Thermal Therapy (Rezūm)
- Prostatic Urethral Lift (PUL)
- Bipolar Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (B-TURP)
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
Lifestyle Changes
1. Healthy Diet and Hydration
Maintaining a healthy diet and proper hydration is paramount in managing the effects of an enlarged prostate. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy weight and potentially reduce prostate enlargement. Staying well-hydrated is essential to keep the urinary tract functioning optimally.
2. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular exercise is a fundamental lifestyle change to alleviate the effects of an enlarged prostate. Exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, helps maintain overall health, improves circulation, and assists in managing weight.
3. Avoiding Bladder Irritants
Avoiding bladder irritants is essential to minimize the effects of an enlarged prostate. Substances like caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, and artificial sweeteners can irritate the bladder, exacerbating urinary symptoms.
4. Timed Voiding
Establishing a regular bathroom schedule and adhering to it can help minimize urinary urgency and frequency.
5. Kegel Exercises
Incorporating Kegel exercises into the daily routine is crucial in managing the effects of an enlarged prostate. Kegel exercises help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, promoting better urinary control and reducing the frequency of urinary leakage.
6. Stress Management
Chronic stress can exacerbate urinary symptoms and overall discomfort. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress levels, leading to better symptom control and an improved quality of life.
7. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and exercise is crucial in managing the effects of an enlarged prostate. Excess weight can put additional pressure on the bladder and worsen urinary symptoms.
8. Avoiding Overhydration at Night
Limiting fluid intake, particularly in the evening, is important to manage the effects of an enlarged prostate. Minimizing fluid consumption close to bedtime can reduce the frequency of nighttime urination, leading to better sleep quality and overall daily functioning.
9. Maintain a Regular Sleep Schedule
Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night to promote a healthy prostate and reduce the risk of hormonal imbalances that may contribute to prostate enlargement.
12. Quit Smoking
If you smoke, quitting is essential in preventing an enlarged prostate. Smoking is linked to an increased risk of prostate enlargement and other prostate-related health issues. Quitting smoking not only benefits prostate health but also significantly improves overall health and reduces the risk of various other diseases.
13. Regular Prostate Check-ups
Routine prostate examinations and screenings can identify any abnormalities early, allowing for timely intervention and potentially preventing the progression to an enlarged prostate or related conditions.
14. Incorporate Prostate-Friendly Supplements
Certain supplements, like saw palmetto, beta-sitosterol, and pygeum africanum, have supported prostate health and potentially prevented prostate enlargement. Hale and Hearty Men is a supplement that contains saw palmetto, selenium, and lycopene which have been scientifically shown to help maintain a healthy prostate. Raveb N Bonnar-Pizzorno et al., published an article that reveals that saw palmetto inhibits the growth of cancer cells. According to Zhigang Cui et al., research, elevated serum levels of selenium is associated with reduced prostate cancer risk. In an article by Ping Chen and some others they discovered this: “consistently, higher circulating lycopene levels significantly reduced the risk of prostate cancer.”
Zinc supplements like our Evergreen Zinc would help to improve prostate health. An article written by David F. Jarrard revealed that zinc could inhibit prostate cancer cell line growth and invasion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy lifestyle through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management is key in preventing and managing the effects of an enlarged prostate. While supplements like Evergreen Zinc may offer potential benefits, they should be used cautiously and under professional guidance. Regular medical check-ups and proactive health choices are fundamental in ensuring a better quality of life for men dealing with this common condition
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What causes an enlarged prostate?
An enlarged prostate, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is primarily caused by age-related changes in the hormones testosterone and estrogen. Other factors may include genetics and lifestyle.
2. Are there risk factors associated with an enlarged prostate?
Yes, risk factors include aging (most common in men over 50), family history, obesity, lack of physical activity, and certain medical conditions or medications.
3. Can an enlarged prostate cause complications beyond urinary issues?
Yes, an enlarged prostate can lead to complications such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), acute urinary retention, bladder stones, kidney damage, and in severe cases, kidney failure.
4. How is an enlarged prostate diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, Digital Rectal Examination (DRE), Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) blood test, and sometimes imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI.
5. What are the treatment options for an enlarged prostate?
Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, minimally invasive procedures (e.g., UroLift, Rezūm), surgical procedures (e.g., TURP, laser therapy), and in specific cases, watchful waiting or active surveillance.
6. Can lifestyle changes effectively manage an enlarged prostate?
Yes, lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, regular exercise, reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, managing stress, and timed voiding can help manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
7. Are there natural remedies to manage an enlarged prostate?
Yes, natural remedies may include herbal supplements (e.g., saw palmetto, beta-sitosterol), dietary changes (e.g., reducing caffeine, increasing plant-based foods), and pelvic floor exercises (e.g., Kegels).
8. Can an enlarged prostate be prevented?
While it’s challenging to prevent entirely, a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular medical check-ups, can reduce the risk of developing an enlarged prostate.