Introduction
A blighted ovum, also known as an anembryonic pregnancy, is a condition where a fertilized egg implants into the uterus but fails to develop into an embryo. It is one of the most common causes of early pregnancy loss, occurring in approximately 50-60% of first-trimester miscarriages. Despite the initial confirmation of pregnancy, the absence of an embryo can lead to the eventual termination of the pregnancy. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for a blighted ovum is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Statistics of Illnesses Related to Blighted Ovum
Blighted ovum is a prevalent cause of miscarriage, accounting for about 20-25% of all early pregnancy losses. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), approximately one in four women will experience a miscarriage during their lifetime, with a blighted ovum being a leading cause. Research suggests that blighted ovum occurs in 1 in 10 confirmed pregnancies, making it a significant issue in reproductive health.
Causes of Blighted Ovum
1. Chromosomal Abnormalities
Chromosomal abnormalities are one of the most common causes of a blighted ovum. These abnormalities occur when there are errors in the number or structure of chromosomes in the fertilized egg. Typically, these abnormalities result from the combination of genetic material from the egg and sperm during fertilization. Such genetic errors prevent the embryo from developing properly, leading to a blighted ovum.
Most chromosomal abnormalities are random and occur by chance. However, certain factors can increase the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, including advanced maternal age and paternal age. Advanced age is associated with a higher likelihood of chromosomal errors in both eggs and sperm, which can contribute to the development of a blighted ovum.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can also lead to a blighted ovum. Hormones play a crucial role in maintaining pregnancy by supporting the development of the embryo and the growth of the gestational sac. If there are imbalances in hormones such as progesterone, which is essential for sustaining the uterine lining, the embryo may not develop correctly, resulting in a blighted ovum.
Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders can disrupt hormonal balance and contribute to early pregnancy loss. Proper management of these conditions before and during pregnancy is crucial to reduce the risk of a blighted ovum.
3. Uterine Abnormalities
Abnormalities in the uterus, such as fibroids, polyps, or structural issues, can also cause a blighted ovum. These abnormalities can interfere with the implantation and growth of the embryo, leading to a pregnancy that fails to develop properly. For example, a septate uterus or uterine fibroids can create an environment that is less conducive to embryo development.
Uterine abnormalities are often diagnosed through imaging techniques such as hysterosalpingography (HSG) or pelvic ultrasound. Identifying and addressing these issues before attempting to conceive can help improve the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy.
Signs and Symptoms of Blighted Ovum
1. Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is a common sign of a blighted ovum. Women may experience light spotting or heavier bleeding, similar to a menstrual period. The presence of bleeding, especially if it is accompanied by cramping, can indicate a miscarriage or a blighted ovum.
The timing and amount of bleeding can vary, and some women may have only mild spotting. However, significant bleeding or changes in bleeding patterns should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to determine the cause and appropriate management.
2. Abdominal Cramping
Abdominal cramping is another symptom associated with a blighted ovum. Cramping can range from mild to severe and may be similar to menstrual cramps. The cramping occurs as the body begins to expel the pregnancy tissue from the uterus.
While mild cramping can be a normal part of early pregnancy, persistent or severe cramping warrants further evaluation. Cramping can also be associated with other conditions, so it is essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause.
3. Absence of Pregnancy Symptoms
The absence of typical pregnancy symptoms, such as nausea, breast tenderness, and fatigue, can also signal a blighted ovum. While some women may continue to experience symptoms despite a blighted ovum, a sudden loss of pregnancy symptoms may indicate that the pregnancy is not progressing as expected.
It is important to monitor changes in pregnancy symptoms and report any concerns to a healthcare provider. While the absence of symptoms alone does not confirm a blighted ovum, it can be a useful indicator in conjunction with other diagnostic findings.
Diagnosis of Blighted Ovum
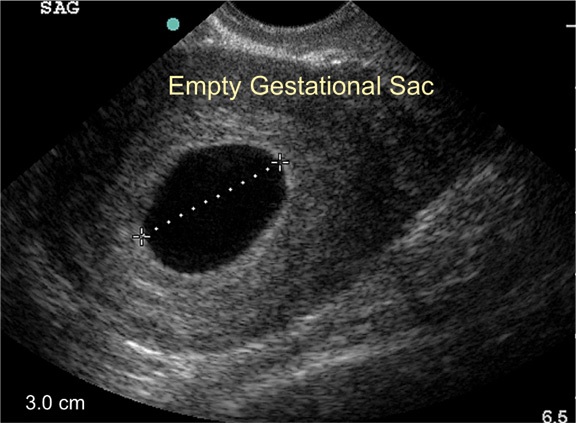
1. Ultrasound Examination
An ultrasound examination is the primary method for diagnosing a blighted ovum. During an ultrasound, a transabdominal or transvaginal probe is used to visualize the gestational sac and check for the presence of an embryo. In a blighted ovum, the ultrasound will show a gestational sac without an embryo.
The ultrasound may be performed at different stages of pregnancy to confirm the diagnosis. Early ultrasounds may not always detect a blighted ovum, so follow-up exams may be necessary if the initial findings are inconclusive.
Ultrasound is a non-invasive and effective tool for diagnosing a blighted ovum and assessing the overall health of the pregnancy.
2. Blood Tests
Blood tests can also aid in the diagnosis of a blighted ovum. Measuring levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone in the blood can provide information about the status of the pregnancy. In a blighted ovum, hCG levels may be inconsistent with the expected growth of the embryo.
Serial blood tests, where hCG levels are measured over time, can help determine if the pregnancy is progressing normally. A decline in hCG levels can indicate a miscarriage or a blighted ovum.
Blood tests provide additional information to support the diagnosis and guide further management.
3. Pelvic Examination
A pelvic examination may be performed to assess the size and shape of the uterus and to check for any signs of abnormal bleeding or cramping. While a pelvic exam alone cannot diagnose a blighted ovum, it can provide valuable information about the health of the reproductive organs.
The findings from a pelvic examination are often used in conjunction with ultrasound and blood tests to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate course of action.
Treatment Options for Blighted Ovum
1. Expectant Management
Expectant management involves waiting for the body to naturally expel the pregnancy tissue without medical intervention. This approach is often recommended if there are no complications and the patient is comfortable with the process. Over time, the body will typically pass the tissue on its own, and the miscarriage will occur naturally.
During expectant management, regular follow-up appointments may be scheduled to monitor progress and ensure that the miscarriage is proceeding as expected. Patients should be advised on what to expect and when to seek medical attention if there are concerns about excessive bleeding or severe pain.
Expectant management can be a suitable option for women who prefer a less invasive approach and are not experiencing significant symptoms.
2. Medical Management
Medical management involves the use of medications to help the body expel the pregnancy tissue. Medications such as misoprostol can be prescribed to induce uterine contractions and facilitate the miscarriage process. This approach can be effective for women who wish to avoid a surgical procedure.
Medical management typically requires follow-up appointments to ensure that the medication has been effective and that the miscarriage is complete. Some women may experience side effects from the medication, such as cramping or gastrointestinal symptoms.
Medical management is a non-invasive alternative to surgery and can be a suitable option for women who prefer this method.
3. Surgical Management
Surgical management, also known as dilation and curettage (D&C), involves a surgical procedure to remove the pregnancy tissue from the uterus. This approach may be recommended if there are complications, such as heavy bleeding or if the miscarriage does not occur naturally or with medication.
During a D&C, a healthcare provider will use surgical instruments to remove the tissue from the uterus. The procedure is typically performed under sedation or anesthesia and may require a short recovery period.
Surgical management is a more invasive option but can be necessary for ensuring that all pregnancy tissue is removed and to prevent complications.
Conclusion
A blighted ovum is a common cause of early pregnancy loss, characterized by the presence of a gestational sac without an embryo. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for a blighted ovum is essential for managing this condition and making informed decisions about care. Whether through expectant, medical, or surgical management, appropriate treatment can help address a blighted ovum and support future reproductive health.
FAQs
- What is a blighted ovum?
A blighted ovum is a pregnancy loss where a fertilized egg implants in the uterus but the embryo does not develop.
- What causes a blighted ovum?
Typically caused by chromosomal abnormalities in the fertilized egg, which prevent embryo development.
- How common is a blighted ovum?
Blighted ovum occurs in about 50% of early pregnancy losses.
- What are the symptoms?
Symptoms can include vaginal bleeding and abdominal cramping, but some women might not experience any symptoms.
- How is a blighted ovum diagnosed?
Diagnosed through ultrasound, showing a gestational sac without an embryo, and confirmed by a drop in pregnancy hormone levels.
- What treatment options are available?
Treatment can include waiting for the miscarriage to occur naturally, medication to induce miscarriage, or a surgical procedure called dilation and curettage (D&C).
- Can a blighted ovum affect future pregnancies?
A blighted ovum typically does not affect future pregnancies. Most women go on to have healthy pregnancies.
- How can I cope with a blighted ovum?
Emotional support, counseling, and connecting with support groups can help manage the grief and stress.
- When should I contact a doctor?
If you experience symptoms of a blighted ovum or have concerns about a potential pregnancy loss, contact your healthcare provider.