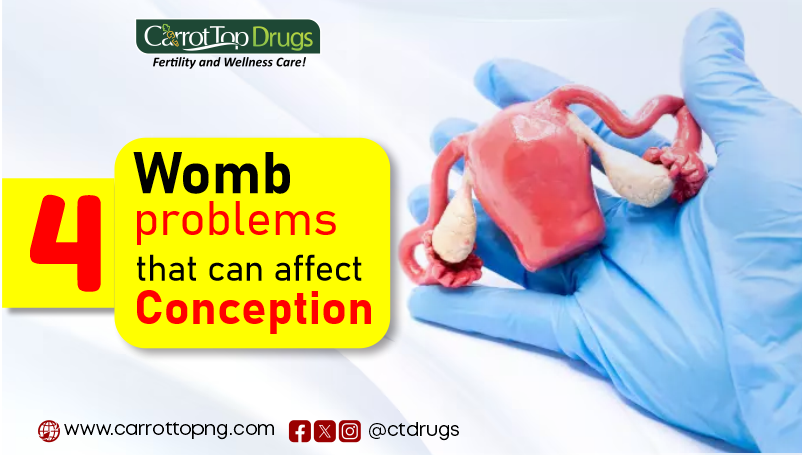
Introduction
Conceiving a child is a deeply desired milestone for many couples, but for some, the journey towards parenthood can be fraught with challenges. One significant factor that can impede conception is the presence of womb problems. There are several womb problems that can affect conception. In this article, we would find out what they are and how they affect conception.
Prevalence of Womb Problems That Can Affect Conception
Studies have indicated varying prevalence rates for different uterine problems, shedding light on the scope of these challenges.
Prevalence of Uterine Fibroids:
Uterine fibroids are one of the most common benign tumors affecting women of reproductive age. Research by Sefah et al suggests that up to 70-80% of women may develop fibroids by the age of 50, with prevalence rates varying depending on factors such as age, race, and family history.
Endometriosis and Its Prevalence:
Endometriosis, characterized by the growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, affects approximately 10% of women of reproductive age worldwide (Giudice, 2010). However, diagnosis rates may vary due to underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis, leading to challenges in determining the true prevalence of the condition.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Prevalence:
PCOS is one of the most common hormonal disorders among women, affecting approximately 6-12% of reproductive-aged women globally (Teede et al., 2010). While PCOS primarily affects ovarian function, it can also lead to uterine abnormalities such as irregular menstrual cycles and endometrial hyperplasia, contributing to difficulties in conception.
Adenomyosis and its Prevalence:
Adenomyosis, characterized by the presence of endometrial tissue within the muscular wall of the uterus, has been reported to affect 20-35% of women of reproductive age (Gunther & Walker, 2023). However, accurate prevalence data may be challenging to obtain due to the nonspecific nature of symptoms and the reliance on imaging studies for diagnosis.
Womb Problems That Can Affect Conception
Uterine Fibroid
One of the womb problems that can affect conception is uterine fibroids. Uterine fibroids can significantly impact conception by affecting the structure and function of the uterus. These noncancerous growths, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, develop within the muscular walls of the uterus and vary in size, number, and location. The presence of fibroids can interfere with conception through several mechanisms:
Distortion of Uterine Cavity:
Large fibroids or multiple fibroids can alter the shape and size of the uterus, leading to distortion of the uterine cavity. This structural abnormality can disrupt the normal process of embryo implantation, making it difficult for a fertilized egg to implant and grow properly within the uterine lining.
Obstruction of Fallopian Tubes:
In some cases, fibroids may grow near the fallopian tubes or cervix, potentially obstructing the passage of sperm or impairing the transport of a fertilized egg through the fallopian tubes to the uterus. This obstruction can hinder the union of sperm and egg, reducing the chances of successful conception.
Disruption of Uterine Contractility:
Fibroids can affect the contractility of the uterine muscles, leading to irregular or inefficient uterine contractions. These irregular contractions may interfere with the movement of sperm towards the egg or hinder the migration of the embryo within the uterine cavity, compromising the process of fertilization and implantation.
Disturbance of Uterine Blood Flow:
The presence of fibroids can alter blood flow within the uterus, leading to changes in the vascular supply to the uterine lining. This disturbance in blood flow may compromise the development of the endometrium (uterine lining) necessary for successful embryo implantation, thereby reducing the likelihood of conception.
Hormonal Imbalance:
Fibroids can influence hormone levels within the body, particularly estrogen and progesterone. Imbalances in these hormones can disrupt the menstrual cycle, affect ovulation, and impair the quality of the uterine lining, all of which are essential for conception to occur.
Endometriosis
Endometriosis can significantly affect conception by causing various disruptions in the reproductive system, hormonal balance, and the environment necessary for successful pregnancy. Here’s how endometriosis is one of the womb problems that can affect conception:
Ovulatory Dysfunction:
Endometriosis can lead to ovulatory dysfunction, meaning that the ovaries may fail to release eggs regularly during the menstrual cycle. This irregular ovulation can reduce the chances of fertilization occurring, as there may be fewer opportunities for sperm to meet and fertilize the egg.
Pelvic Adhesions and Scarring:
Endometriosis can cause the formation of pelvic adhesions and scar tissue, which may distort the normal anatomy of the reproductive organs. These adhesions can physically obstruct the fallopian tubes or interfere with the movement of the egg from the ovary to the uterus. As a result, no fertilization, leading to difficulties in conception.
Inflammation and Hormonal Imbalances:
Endometriosis is associated with chronic inflammation in the pelvic cavity, which can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance necessary for conception. Imbalances in hormones such as estrogen and progesterone can affect the development of the uterine lining (endometrium), making it less conducive for embryo implantation and pregnancy.
Endometrial Implantation Issues:
In women with endometriosis, the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus (such as on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or pelvic lining) can interfere with the process of embryo implantation. The aberrant endometrial tissue may create a hostile environment within the pelvic cavity, making it difficult for the embryo to attach and establish a pregnancy.
Reduced Egg Quality:
Some studies suggest that endometriosis may be associated with decreased egg quality, potentially affecting the viability of embryos formed through fertilization. Poor egg quality can reduce the likelihood of successful implantation and increase the risk of early pregnancy loss (miscarriage).
Pain and Sexual Dysfunction:
The chronic pelvic pain associated with endometriosis can lead to sexual dysfunction and reduced frequency of intercourse, which may further decrease the chances of conception. Additionally, pain during intercourse (dyspareunia) can make sexual activity uncomfortable or undesirable, impacting a couple’s ability to conceive naturally.
PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can significantly affect conception due to its impact on hormone levels, ovulation, and the reproductive system. Here’s how PCOS is one the womb problems that can affect conception:
Ovulatory Dysfunction:
One of the hallmark features of PCOS is irregular or absent ovulation, known as anovulation. Women with PCOS may experience infrequent or unpredictable menstrual cycles due to hormonal imbalances, particularly elevated levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) and insulin resistance. Without regular ovulation, there is disruption to the release of mature eggs from the ovaries, reducing the chances of fertilization and conception.
Hormonal Imbalances:
PCOS is characterized by imbalances in reproductive hormones, including elevated levels of androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone. These hormonal disturbances can affect the development and maturation of ovarian follicles, leading to the formation of multiple small cysts on the ovaries. The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can interfere with the normal menstrual cycle and ovulation, making conception challenging.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
Women with PCOS often experience irregular menstrual cycles, characterized by unpredictable or prolonged periods. The absence of regular menstrual cycles can indicate underlying ovulatory dysfunction, further complicating the process of conception. Without predictable ovulation, timing intercourse to coincide with the fertile window becomes more challenging, reducing the likelihood of successful fertilization.
Endometrial Abnormalities:
Prolonged periods of anovulation in women with PCOS can result in inadequate production of progesterone, a hormone necessary for the development and maintenance of the uterine lining (endometrium). As a result, women with PCOS may have thin or inadequate endometrial linings, which can impair embryo implantation and increase the risk of early pregnancy loss (miscarriage).
Increased Risk of Insulin Resistance:
Insulin resistance is common in women with PCOS and occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance can disrupt ovarian function and hormone production, further exacerbating ovulatory dysfunction and infertility. Women with PCOS who also have insulin resistance may be at an increased risk of developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy, which can further complicate fertility and pregnancy outcomes.
Impact on Egg Quality:
Some studies suggest that women with PCOS may have reduced egg quality compared to women without the condition. Poor egg quality can decrease the likelihood of successful fertilization and embryo development, leading to lower pregnancy rates and an increased risk of miscarriage.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis can affect conception through various mechanisms related to changes in the structure, function, and hormonal environment of the uterus. Here’s how adenomyosis is one of the womb problems that can affect conception:
Uterine Enlargement and Distortion:
Adenomyosis is characterized by the presence of endometrial tissue within the muscular wall of the uterus, leading to uterine enlargement and distortion. The enlarged uterus may create an unfavorable environment for embryo implantation and development, as it can alter the shape and size of the uterine cavity. This distortion can disrupt the normal process of embryo implantation, reducing the chances of successful conception.
Impaired Uterine Contractility:
Adenomyosis can affect the contractility of the uterine muscles, leading to irregular or inefficient uterine contractions. These abnormal contractions may interfere with the transport of sperm through the reproductive tract or hinder the migration of the embryo within the uterine cavity. As a result, fertilization and implantation may be impaired, decreasing the likelihood of conception.
Endometrial Dysfunction:
Adenomyosis can disrupt the normal functioning of the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus essential for embryo implantation and pregnancy. The presence of ectopic endometrial tissue within the uterine wall can lead to inflammation, scarring, and changes in the hormonal environment, all of which can affect the receptivity of the endometrium to embryo implantation. This endometrial dysfunction may decrease the chances of successful embryo implantation and pregnancy.
Menstrual Irregularities:
Women with adenomyosis often experience heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding, along with severe menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea). These menstrual irregularities can indicate underlying hormonal imbalances and structural abnormalities within the uterus, which may affect ovulation and the release of mature eggs from the ovaries. As a result, women with adenomyosis may have difficulty conceiving due to irregular ovulation and menstrual cycles.
Pain and Sexual Dysfunction:
The chronic pelvic pain associated with adenomyosis can lead to sexual dysfunction and reduced frequency of intercourse, which may further decrease the chances of conception. Additionally, pain during intercourse (dyspareunia) can make sexual activity uncomfortable or undesirable, impacting a couple’s ability to conceive naturally.
Signs and Symptoms
Uterine abnormalities can manifest through various symptoms and signs, affecting both reproductive health and overall well-being. Here’s an explanation of how these abnormalities may present:
Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
Irregular menstrual cycles refer to deviations from the typical pattern of menstruation, including variations in cycle length, duration, or flow. Uterine abnormalities such as fibroids, adenomyosis, or endometrial polyps can disrupt the normal hormonal fluctuations and processes involved in menstruation, leading to irregular cycles. Women may experience unpredictable or infrequent periods, with cycles lasting shorter or longer than usual. Irregular menstrual cycles can also indicate underlying hormonal imbalances or structural issues within the uterus, which may impact fertility and conception.
Pelvic Pain:
Pelvic pain is a common symptom associated with uterine abnormalities, including conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, or adenomyosis. The pain may vary in intensity and duration, ranging from dull aches to sharp cramps, and may be localized to the pelvic region or radiate to the lower back or thighs. Pelvic pain can occur before, during, or after menstruation and may worsen during certain activities such as intercourse or bowel movements. Chronic pelvic pain can significantly impair quality of life and may indicate the presence of underlying uterine pathology that requires medical evaluation and management.
Heavy Menstrual Bleeding:
Heavy menstrual bleeding, also known as menorrhagia, refers to excessive or prolonged menstrual flow that interferes with daily activities and normal functioning. Uterine abnormalities such as fibroids, adenomyosis, or endometrial hyperplasia can cause alterations in the uterine lining, leading to increased blood loss during menstruation. Women with heavy menstrual bleeding may require frequent changes of menstrual products, experience clotting or flooding, and may develop symptoms of anemia such as fatigue or weakness. Addressing the underlying uterine pathology is essential for managing heavy menstrual bleeding and improving overall menstrual health.
Painful Intercourse:
Painful intercourse, medically known as dyspareunia, is a common symptom associated with uterine abnormalities such as fibroids, endometriosis, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). The presence of fibroids or adhesions within the uterus can cause discomfort or pain during penetrative intercourse, resulting from pressure or friction against the uterine walls. Similarly, endometriosis can lead to inflammation, scarring, and adhesions within the pelvic cavity, causing pain or discomfort with deep penetration or certain sexual positions. Painful intercourse can significantly impact sexual function and intimacy, highlighting the need for medical evaluation and treatment of underlying uterine pathology.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing uterine problems that affect conception typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging studies, and sometimes minimally invasive procedures. Here’s a list and explanation of diagnostic methods commonly used:
Medical History and Physical Examination:
Healthcare providers begin by gathering a detailed medical history, including menstrual patterns, symptoms related to fertility or reproductive health, past surgeries, and any relevant medical conditions. A thorough physical examination can assess the pelvic organs, including the uterus and ovaries, for any abnormalities or signs of uterine problems such as fibroids, adenomyosis, or endometrial polyps.
Pelvic Ultrasound:
Pelvic ultrasound, including transvaginal ultrasound, is a non-invasive imaging technique used to visualize the structures of the reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Ultrasound can detect abnormalities such as fibroids, ovarian cysts, or structural irregularities within the uterus that may affect fertility. It provides valuable information about the size, location, and characteristics of uterine lesions, helping guide further evaluation and treatment.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG):
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is a specialized X-ray procedure used to evaluate the shape and condition of the uterus and fallopian tubes. During an HSG, the specialist injects a contrast dye into the uterine cavity through the cervix, allowing visualization of the uterine contour and detecting abnormalities such as fibroids, polyps, or uterine adhesions. HSG can also assess the patency of the fallopian tubes, providing information about tubal blockages or abnormalities that may impact fertility.
Hysteroscopy:
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a thin, lighted instrument called a hysteroscope through the cervix into the uterus. It allows direct visualization of the uterine cavity, enabling the identification and evaluation of uterine abnormalities such as fibroids, polyps, or adhesions. It can also perform therapeutic interventions, such as removing uterine lesions or conducting endometrial biopsies for further evaluation.
Laparoscopy:
It is a surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia that involves making small incisions in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source, to visualize the pelvic organs. Laparoscopy can help diagnose conditions such as endometriosis, ovarian cysts, or pelvic adhesions that may affect fertility. It allows for direct visualization and evaluation of the pelvic structures and may be combined with therapeutic interventions if necessary.
Endometrial Biopsy:
Endometrial biopsy involves obtaining a small sample of tissue from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) for microscopic examination. This procedure evaluate the endometrium for abnormalities such as endometrial hyperplasia, which can affect fertility. Endometrial biopsy may be recommended if other diagnostic tests indicate abnormalities or if there are concerns about the uterine lining’s receptivity for embryo implantation.
Treatment of Uterine Problems That Can Affect Conception
Treatment for Uterine Fibroids:
Uterine fibroids, common womb problems that can affect conception, are noncancerous growths in the uterus that can interfere with fertility by distorting the uterine cavity or obstructing the fallopian tubes. Treatment options vary depending on the size, location, and severity of symptoms.
We recommend pain relievers for individuals experiencing mild symptoms or seeking fertility preservation as a conservative management. However, for those with significant symptoms or fertility concerns, interventions such as myomectomy (surgical removal of fibroids) or uterine artery embolization (blocking blood flow to fibroids) are done to improve fertility outcomes (Stewart, 2017; Vitagliano et al., 2021).
Treatment for Endometriosis:
Endometriosis one of the womb problems that can affect conception, occurs when tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, leading to inflammation, scarring, and pelvic pain. In individuals struggling with infertility due to endometriosis, treatment aims to alleviate symptoms and improve fertility outcomes.
Medical management options include pain relief with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or hormonal therapies such as oral contraceptives, progestins, or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists to suppress endometriosis-related symptoms and reduce inflammation.
Surgical interventions, such as laparoscopic excision of endometriosis lesions or laparoscopic ovarian drilling, may be recommended to remove endometriotic tissue and improve fertility by restoring pelvic anatomy and ovarian function (Johnson et al., 2017; Dunselman et al., 2014).
Treatment for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is characterized by hormonal imbalances, ovarian dysfunction, and metabolic disturbances, contributing to fertility challenges in affected individuals. Management of PCOS-related infertility focuses on regulating menstrual cycles, inducing ovulation, and addressing metabolic abnormalities. Lifestyle modifications, including weight loss, dietary changes, and regular exercise, are the as first-line therapy to improve insulin sensitivity and hormone balance.
Pharmacological interventions such as oral ovulation-inducing medications (e.g., clomiphene citrate, letrozole) or injectable gonadotropins may be prescribed to stimulate ovulation in individuals with PCOS-associated infertility. We also recommend the use of supplements like Evergreen Formular for Women. It can reduce the hyperandrogenism in PCOS. In vitro fertilization (IVF) may be considered for those who do not respond to conventional treatments (Legro et al., 2018; Teede et al., 2018).
Treatment for Adenomyosis:
Adenomyosis, characterized by the presence of endometrial tissue within the muscular wall of the uterus, is another uterine problem that can affect conception. Treatment approaches for adenomyosis-related infertility aim to alleviate symptoms such as pelvic pain and heavy menstrual bleeding while optimizing fertility outcomes.
Medical management options include pain relief with NSAIDs or hormonal therapies such as oral contraceptives, progestins, or GnRH agonists to suppress menstrual bleeding and reduce adenomyosis-related symptoms.
In cases where conservative measures are ineffective, surgical interventions such as uterine-sparing procedures (e.g., adenomyomectomy) or definitive treatments like hysterectomy may be considered to improve fertility and quality of life (Vercellini et al., 2014; Leyendecker et al., 2021).
Treatment for Uterine Abnormalities:
Uterine abnormalities encompass structural anomalies of the uterus, such as septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, or uterine adhesions (Asherman’s syndrome), which can adversely affect fertility by altering the uterine environment or impeding embryo implantation. Treatment options depend on the specific type and severity of the uterine abnormality.
Surgical interventions, such as hysteroscopic septum resection or metroplasty, may be performed to correct structural defects and improve fertility outcomes. In cases of uterine adhesions, hysteroscopic adhesiolysis (removal of adhesions) followed by adjuvant measures to prevent recurrence may be necessary to restore uterine function and enhance fertility potential (Conforti et al., 2013; Salazar et al., 2016).
Conclusion
In summary, uterine problems significantly hinder conception by disrupting reproductive processes such as ovulation and implantation. Conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, PCOS, adenomyosis, and uterine abnormalities impede fertility, necessitating personalized treatment approaches for affected individuals. Early detection, advanced medical interventions, and heightened awareness are crucial in addressing uterine issues and fostering successful conception outcomes.
FAQs
- What are the common symptoms of uterine problems that can affect conception?
- Common symptoms include irregular cycles, pelvic pain, heavy bleeding, painful intercourse, and difficulty getting pregnant. Seek medical advice if you experience any.
- Can uterine fibroids affect fertility, and how can we treat them?
- Yes, fibroids can hinder fertility. Treatments include medication, minimally invasive procedures like myomectomy, or uterine artery embolization.
- What role does endometriosis play in infertility, and how can we manage it?
- Endometriosis can cause inflammation, scarring, and pain, impacting fertility. Management involves medication for pain relief or surgery to remove lesions.
- How does polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) impact fertility, and what treatments are available?
- PCOS disrupts ovulation and hormone balance, affecting fertility. Treatments include lifestyle changes, medication to induce ovulation, or assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
- Is adenomyosis associated with infertility, and what are the treatment options?
- Yes, adenomyosis can affect fertility. Treatment may involve medication for pain relief or surgery like adenomyomectomy to improve fertility.
- Can uterine abnormalities such as septate uterus or uterine adhesions affect conception?
- Yes, structural issues can impact fertility. Treatment includes surgery to correct defects or remove adhesions to enhance fertility potential.
- When should I seek medical help for suspected uterine problems affecting conception?
- If you’ve been trying to conceive without success for six months to a year, especially with symptoms like irregular periods or pelvic pain, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
- Are there lifestyle changes to improve fertility despite uterine problems?
- Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle such as balanced diet, maintaining weight, managing stress, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, and practicing safe sex can improve fertility outcomes.
Have you been trying to conceive without any luck? leave a comment or call 08173658113. Also, you can send a message on our Facebook or Instagram.